DOM型XSS
DOM全称Document Object Model,是一个平台和语言都中立的接口,可以使程序和脚本能够动态访问和更新文档的内容、结构以及样式。
DOM型XSS其实是一种特殊类型的反射型XSS,它是基于DOM文档对象模型的一种漏洞。
在网站页面中有许多页面的元素,当页面到达浏览器时浏览器会为页面创建一个顶级的Document object文档对象,接着生成各个子文档对象,每个页面元素对应一个文档对象,每个文档对象包含属性、方法和事件。可以通过JS脚本对文档对象进行编辑从而修改页面的元素。也就是说,客户端的脚本程序可以通过DOM来动态修改页面内容,从客户端获取DOM中的数据并在本地执行。基于这个特性,就可以利用JS脚本来实现XSS漏洞的利用。
Low:
查看源码:
<?php # No protections, anything goes ?>
<div class="vulnerable_code_area">
<p>Please choose a language:</p>
<form name="XSS" method="GET">
<select name="default">
<script>
if (document.location.href.indexOf("default=") >= 0) {
var lang = document.location.href.substring(document.location.href.indexOf("default=")+8);
document.write("<option value='" + lang + "'>" + decodeURI(lang) + "</option>");
document.write("<option value='' disabled='disabled'>----</option>");
}
document.write("<option value='English'>English</option>");
document.write("<option value='French'>French</option>");
document.write("<option value='Spanish'>Spanish</option>");
document.write("<option value='German'>German</option>");
</script>
</select>
<input type="submit" value="Select" />
</form>
</div>
DOM XSS 是通过修改页面的 DOM 节点形成的 XSS。首先通过选择语言后然后往页面中创建了新的 DOM 节点
document.write("" + $decodeURI(lang) + "");
document.write("----");
源码分析:
这里的lang变量通过document.location.href来获取到,并且没有任何过滤就直接URL解码后输出在了option标签中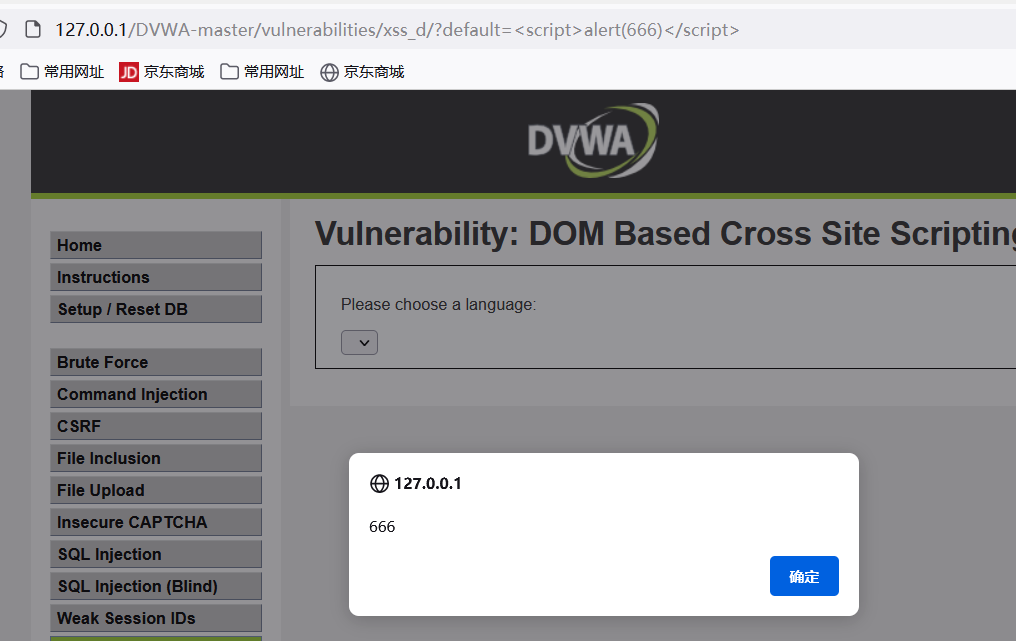
Medium:
查看源码:
<?php
// Is there any input?
if ( array_key_exists( "default", $_GET ) && !is_null ($_GET[ 'default' ]) ) {
$default = $_GET['default'];
# Do not allow script tags
if (stripos ($default, "<script") !== false) {
header ("location: ?default=English");
exit;
}
}
?>
函数:
stripos() // 函数查找字符串在另一字符串中第一次出现的位置(不区分大小写) header() // 函数向客户端发送原始的 HTTP 报头。
分析:
针对script字段进行了过滤,通过stripos()函数查找script 字符串在default变量中第一次出现的位置,如果匹配成功的话通过location将URL后面的参数修正为?default=English,同样这里可以通过其他的标签搭配事件类型来达到弹窗效果
看一下<script>的过滤效果 <script>alert(666)</script>
确实被修正了
使用img标签 <img src=1 onerror=alert(666)>

未能实现弹窗,找找原因
按F12查看网页源代码
发现我们的语句被插入到了value值中,但是并没有插入到option标签的值中,所以img标签并没有发起任何作用
闭合</option>和</select>,然后再使用img标签通过事件弹窗
</option></select><img src=1 onerror=alert(666)>
闭合的效果:

High:
查看源码:
<?php
// Is there any input?
if ( array_key_exists( "default", $_GET ) && !is_null ($_GET[ 'default' ]) ) {
# White list the allowable languages
switch ($_GET['default']) {
case "French":
case "English":
case "German":
case "Spanish":
# ok
break;
default:
header ("location: ?default=English");
exit;
}
}
?>
源码分析:
先判断defalut值是否为空,如果不为空的话,再用switch语句进行匹配,如果匹配成功,则插入case字段的相应值,如果不匹配,则插入的是默认的值。这样的话,我们的语句就没有可能插入到页面中了。
可以用&连接一个新的自定义变量来Bypass
&</option></select><img src=1 onerror=alert('hahaha')></option>
 也可以用#来Bypass
也可以用#来Bypass
#</option></select><img src=1 onerror=alert('test')></option>

Impossible:
查看源码:
<?php # Don't need to do anything, protction handled on the client side ?>
只有一行注释,注释写的是保护的代码在客户端的里面。(protction应该是敲错了,查了没有这个单词,应该是protection)
防护总结:
检测的流程就是通过查看代码是否有document.write、eval、window之类能造成危害的地方,然后通过回溯变量和函数的调用过程,查看用户是否能控制输入。如果能控制输入,就看看是否能复现,能复现就说明存在DOM XSS,需要对输入的数据进行编码。
当业务需要必须得将用户输入的数据放入html,那就要尽量使用安全的方法,比如innerText(),testContent()等。在使用框架时尽量使用框架自带的安全函数。
来源:freebuf.com 2021-06-29 12:06:54 by: wakemeup










请登录后发表评论
注册