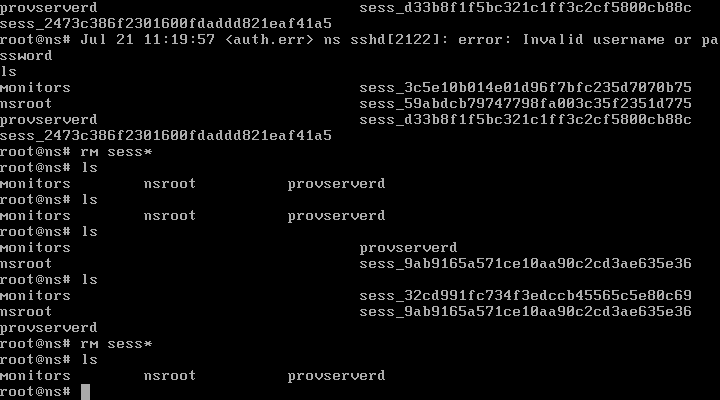
req_stat配置为计数器按照server{}维度统计状态码,使用时配置如下:
|
req_status_lazy on; req_status_zone req_status “$server_addr:$server_port:$upstream_addr” 50M; req_status req_status; server { listen 127.0.0.1:80; location /check_status { req_status_show req_status; } } |
在req_status_zone指令的函数中,将这个字符串进行编译,放入ctx→value,ctx为这个模块的上下文:
|
static char * ngx_http_reqstat_zone(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) { … ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_reqstat_ctx_t)); ngx_memzero(&ccv, sizeof(ngx_http_compile_complex_value_t)); ccv.cf = cf; ccv.value = &value[2]; // ccv的complex_value指针指向ctx->value ccv.complex_value = &ctx->value; // compile之后,ctx的value存储这一格式 if (ngx_http_compile_complex_value(&ccv) != NGX_OK) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } // ctx->val是个string,记录这个key的名字 ctx->val = ngx_palloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_str_t)); if (ctx->val == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } *ctx->val = value[2]; … } |
ngx_http_reqstat把对应的req_status_zone配置相应的共享内存:
|
static char * ngx_http_reqstat(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) { … // 这块是从ngx_conf_handler中取出来的配置,按理说我们配置里面都把ngx_http_reqstat放在http下面,应该也是main conf ngx_http_reqstat_conf_t *rlcf = conf; value = cf->args->elts; // 这个smcf是从cf->ctx中拿出来的reqstat main 配置,按理说和上面的rlcf应该相同,不明白为何不一样。 // 终于弄明白了,cmd->type那块是NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF,而ngx_conf_handler那块是NGX_MAIN_CONF,所以一定会走到loc_conf里面,所以cmd第四个那个位置就是这个指令修改的配置最终在哪里的意思 // 因此这块修改都是http块下面生成的loc conf smcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_main_conf(cf, ngx_http_reqstat_module); // 将rlcf的monitor初始化,并且将没有的添加进smcf中。 rlcf->monitor = ngx_array_create(cf->pool, cf->args->nelts – 1, sizeof(ngx_shm_zone_t *)); for (i = 1; i < cf->args->nelts; i++) { // 添加对应数量的shm_zone,放入rlcf->monitor数组 shm_zone = ngx_shared_memory_add(cf, &value[i], 0, &ngx_http_reqstat_module); z = ngx_array_push(rlcf->monitor); *z = shm_zone; z = smcf->monitor->elts; for (j = 0; j < smcf->monitor->nelts; j++) { if (!ngx_strcmp(value[i].data, z[j]->shm.name.data)) { break; } } // smcf存一个全量 if (j == smcf->monitor->nelts) { z = ngx_array_push(smcf->monitor); if (z == NULL) { return NGX_CONF_ERROR; } *z = shm_zone; } } … } |
配置指定完后调用ngx_http_reqstat_init函数,来把两个handler放入对应阶段中:
|
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_reqstat_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) { … cmcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_main_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module); h = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE].handlers); *h = ngx_http_reqstat_log_handler; h = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE].handlers); *h = ngx_http_reqstat_init_handler; … } |
ngx_http_reqstat_init_handler在rewrite阶段,每个请求都经过,如果没有store的话,初始化store:
|
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_reqstat_init_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) { … ngx_http_reqstat_conf_t *rmcf, *rlcf; ngx_http_reqstat_store_t *store; store = ngx_http_get_module_ctx(r, ngx_http_reqstat_module); rmcf = ngx_http_get_module_main_conf(r, ngx_http_reqstat_module); rlcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_reqstat_module); if (store == NULL) { if (r->variables[rmcf->index].valid) { return NGX_DECLINED; } // 创建store store = ngx_http_reqstat_create_store(r, rlcf); if (store == NULL) { return NGX_ERROR; } // 这个store只关联于这个request,一旦这个request销毁,就不复存在,因此每个新的请求都要创建一个store ngx_http_set_ctx(r, store, ngx_http_reqstat_module); } … } |
ngx_http_reqstat_create_store函数:
|
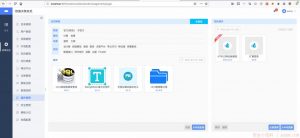
static ngx_http_reqstat_store_t * ngx_http_reqstat_create_store(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_reqstat_conf_t *rlcf) { … store = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_reqstat_store_t)); // 创建monitor index和value index if (ngx_array_init(&store->monitor_index, r->pool, rlcf->monitor->nelts, sizeof(ngx_http_reqstat_rbnode_t *)) == NGX_ERROR) { return NULL; } if (ngx_array_init(&store->value_index, r->pool, rlcf->monitor->nelts, sizeof(ngx_str_t)) == NGX_ERROR) { return NULL; } // 在shm_zone里查找val,从而找到node(应该是模糊匹配?),每个shm_zone对应一个store里面的value_index和monitor_index shm_zone = rlcf->monitor->elts; for (i = 0; i < rlcf->monitor->nelts; i++) { z = shm_zone[i]; ctx = z->data; if (ngx_http_complex_value(r, &ctx->value, &val) != NGX_OK) { ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, r->connection->log, 0, “failed to reap the key \”%V\””, ctx->val); continue; } value = ngx_array_push(&store->value_index); *value = val; fnode = ngx_http_reqstat_rbtree_lookup(shm_zone[i], &val); fnode_store = ngx_array_push(&store->monitor_index); *fnode_store = fnode; … } |
ngx_http_reqstat_log_handler真正记录:
|
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_reqstat_log_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) { … // 获取共享内存,fnode数组,value数组。 shm_zone = rcf->monitor->elts; fnode_store = store->monitor_index.elts; value = store->value_index.elts; // 遍历之前存好的monitor_index,这个适合shm_zone的数量是对应起来的,给每个shm_zone都加入这个计数 for (i = 0; i < store->monitor_index.nelts; i++) { if (fnode_store[i] == NULL) { continue; } // 获取z和上下文ctx z = shm_zone[i]; ctx = z->data; // 核心:判断是否是lazy if (rcf->lazy) { // 是的话,使用r重新compile val,这次有了upstream相关的,任何变量都能用。 if (ngx_http_complex_value(r, &ctx->value, &val) != NGX_OK) { ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, r->connection->log, 0, “failed to reap the key \”%V\””, ctx->val); continue; } // 如果重新编译的val和之前编译过的是value一致的话,就不用重新在tree里面搜索了,代表两次编译(虽然打开lazy开关),但是一致, if (value[i].len == val.len && ngx_strncmp(value[i].data, val.data, val.len) == 0) { fnode = fnode_store[i]; // 如果不行的话,需要重新搜索,之前搜索那个匹配不上。 } else { // 终于有了真正的fnode fnode = ngx_http_reqstat_rbtree_lookup(shm_zone[i], &val); if (fnode == NULL) { ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_WARN, r->connection->log, 0, “failed to alloc node in zone \”%V\”, “ “enlarge it please”, &z->shm.name); fnode = fnode_store[i]; // 开始计数 } else { ngx_http_reqstat_count(fnode, NGX_HTTP_REQSTAT_BYTES_OUT, r->connection->sent); ngx_http_reqstat_count(fnode, NGX_HTTP_REQSTAT_BYTES_IN, r->connection->received); if (store) { store->recv = r->connection->received; } } } } else { fnode = fnode_store[i]; } … } |
来源:freebuf.com 2021-06-07 10:59:32 by: stan1y










请登录后发表评论
注册